Introduction
The Past Perfect tense is often feared by students. It is one of the complicated tenses. However, it is not that tricky. This chapter examines the Past Perfect Simple and the Past Perfect Continuous. Let’s first look at the way they are formed and then the situations in which we use them.
1 Past perfect simple
The Past Perfect Simple expresses what happened before the past event – hence the name Past Perfect. Therefore, this tense rarely occurs without the context:
- After I had bought the gift, I went to the party.
- How do we know which part of a sentence the Past Perfect Simple will be in? It is in the one where the first event happened. Something happened in the past (I went to the party – Past tense), but BEFORE that I was doing something (I had bought a gift – Past Perfect).

Before we talk in more detail about the situations in which we use this tense, let’s explore its formation.
1.1 Forming Past Perfect Simple
What do we need to form Past Perfect Simple?
subject + auxiliary verb HAD + regular verb with -ed / 3. form of irregular verb
| Positive form | ||
|---|---|---|
| I | had | exercised. |
| You | had | exercised. |
| He | had | exercised. |
| She | had | exercised. |
| We | had | exercised. |
| You | had | exercised. |
| They | had | exercised. |
- The negative of the Past Perfect Simple is formed by adding NOT to the auxiliary verb HAD (I had not exercised.) HAD
(I had not exercised.) - The short form is HADN‘T (I hadn‘t exercised.)
| Negative form | ||
|---|---|---|
| I | hadn’t | exercised. |
| You | hadn’t | exercised. |
| He | hadn’t | exercised. |
| She | hadn’t | exercised. |
| We | hadn’t | exercised. |
| You | hadn’t | exercised. |
| They | hadn’t | exercised. |
- When forming a question, we just switch the subject of the sentence with the auxiliary verb HAD
| Question | ||
|---|---|---|
| Had | I | exercised? |
| Had | you | exercised? |
| Had | he | exercised? |
| Had | she | exercised? |
| Had | we | exercised? |
| Had | you | exercised? |
| Had | they | exercised? |
1.2 Use of Past Perfect Simple
When do we use the Past Perfect Simple?
When something had happened before a certain moment in the past
- After I had examined the patient, I recommended more exercise.
- As can be seen from the sentence, the doctor first examined the patient and then recommended more movement.

- Because she hadn´t brought her purse, she had to go home to get it.
- As we can see from the sentence, firstly, she left her purse at home and then had to return for it.

- Had you done your homework before you went to the cinema?
-
- Here, for example, is a mother who makes sure that her son did his homework and then went to the cinema.
-

1.3 Vocabulary related to Past Perfect Simple
The Past Perfect Simple is characterized by the frequent use of the following adverbs:
AFTER, WHEN
Both of these adverbs can be placed at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle:
-
-
- When I had finished cooking, I called my friend.
- I called my friend after I had finished cooking.
-
BEFORE
The adverb BEFORE can be placed at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle.
-
-
- Before I went to lunch, I had had an interview.
- I had had an interview before I went to lunch.
-
In the case that an event took place at a particular time, the Past Perfect Simple is not a rerequisite and we can use the Past Simple tense. The same is true for the adverb AFTER. Therefore, both of these options are possible:
-
-
- I had seen them only once in 2015 before I went on a road trip with them in 2017.
- I saw them only once in 2015 before I went on a road trip with them in 2017.
-
However, if it is not an event occurring at a particular time, we need to use the Ppat Perfect Simple. In the following sentence we see that this is not an event, but an experience:
-
-
- I had worked for several companies before I started working for you.
- Not:
I worked for several companies before I started working for you.
- Not:
- I had worked for several companies before I started working for you.
-
BECAUSE
We use the conjunction BECAUSE for so-called reason sentences. The subordinate clause is in the Past Perfect Simple if we want to express that it had happened before a certain moment in the past. Again, we can place it at the beginning of the sentence or in the middle:
-
-
- Because I hadn’t studied, I failed the test.
- I failed the test because I hadn’t studied.
-
WHO, WHICH
We often come across related subordinate clauses:
-
-
- The girl, who I had met last summer, called me.
- The movie which you had recommended to me was really good!
-
THAT
The Past Perfect also appears with object subordinate sentences:
-
-
- I realized that somebody had broken into our house.
-
2 Past Perfect Continuous
If you have studied the rules about the Past Perfect Simple, the Past Perfect Continuous won’t be so complicated for you. While we can tell by the Past Perfect Simple what had happened at a particular moment in the past, the Past Perfect Continuous serves to tell us what had been happening before a certain moment in the past.
- He was dirty because he had been playing in the sandbox the whole afternoon.
- We emphasize the course of this event- so we also add that it took the whole afternoon.

Before we take a closer look at the situations in which we use this tense, let’s explain how it is formed.
2.1 Forming Past Perfect Continuous
What do we need to form Past Perfect Continuous?
subject + HAD + BEEN + action verb with ending -ING + rest of sentence
| Positive form | ||
|---|---|---|
| I | had been | waiting. |
| You | had been | waiting. |
| He | had been | waiting. |
| She | had been | waiting. |
| We | had been | waiting. |
| You | had been | waiting. |
| They | had been | waiting. |
- We create the negative form by putting NOT after HAD (the auxiliary verb)
- The short form is HADN‘T (You hadn’t been waiting (nečekal jsi)).
| Negative form | ||
|---|---|---|
| I | hadn’t been | waiting. |
| You | hadn’t been | waiting. |
| He | hadn’t been | waiting. |
| She | hadn’t been | waiting. |
| We | hadn’t been | waiting. |
| You | hadn’t been | waiting. |
| They | hadn’t been | waiting. |
- We form a question by switching the subject with the auxiliary verb HAD
- The verb BEEN follows the subject:
| Question | ||
|---|---|---|
| Had | I been | waiting? |
| Had | you been | waiting? |
| Had | he been | waiting? |
| Had | she been | waiting? |
| Had | we been | waiting? |
| Had | you been | waiting? |
| Had | they been | waiting? |
2.2 Use of Past Perfect Continuous
Now we know how to form Past Perfect Continuous, we can now look at the situations where we use it:
We are talking about something that has been going on for some time before a specific point in the past
- She was exhausted because she had been exercising for two hours.
- The exercise has lasted for two hours and it made the person exhausted.
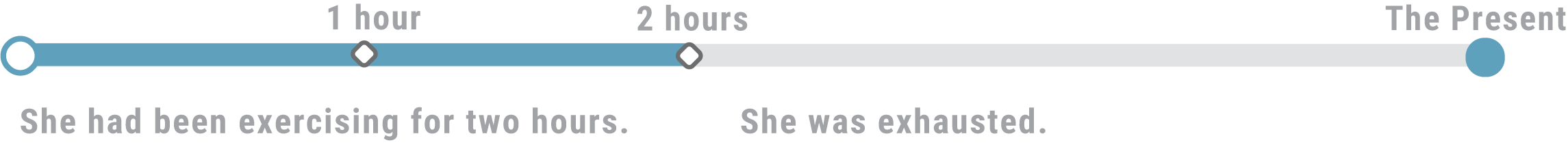
We want to emphasize the duration of a certain event
We don’t just use only Past Perfect Continuous with a specific expression of time. We also use it when we want to say that the event took a longer time:
- Our football match was canceled after an hour due to the bad weather. We had been playing so well though!
- They had been playing really well (all the time) before the football match was cancelled.

We are talking about a state that was caused by a certain event
- He came home completely wet. It had been raining the whole afternoon.
- He was wet (state) because it had been raining the whole afternoon (event).

3 Past tense compared to other tenses
Now let’s look at the same sentence in different tenses. Notice how its meaning changes.
- When I entered the room, my dad sat down and ate his dinner.
When I entered the room, my dad sat down and ate his dinner.- The actions happened one after the other, we use simple past tense.
- When I entered the room, my dad was eating his dinner.
When I entered the room, my dad was eating his dinner.- His activity was in progress at the moment I entered the room, so we use past continuous tense.
- When I entered the room, my dad had eaten his dinner.
When I entered the room, my dad had already finished his dinner.- Father had completed the activity before I entered the room. To express this sequence, we use past perfect tense.
4 Practicing past perfect tense
Try the following exercises and test your newly acquired knowledge.
4.1 Instructions
Exercise 1: Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb
Fill in the blank with the correct form of the verb in past and past perfect tense:
1) By the time I __________ (arrive) at the party, everyone __________ (leave).
2) She __________ (study) for two hours before she __________ (take) a break.
3) They __________ (already eat) by the time we __________ (get) to the restaurant.
4) The movie __________ (start) before we __________ (arrive) at the cinema.
5) He __________ (never see) a bear before he __________ (go) to Alaska.
Exercise 2: Sentence transformation
Change the following sentences to the past perfect tense:
1) I woke up early this morning.
2) They started the project last week.
3) She bought a new car yesterday.
4) He had a sandwich for lunch.
5) We went to bed late last night.
Exercise 3: Answers the questions
Answer the following questions in the past perfect tense:
1) Had you ever been to New York before your trip last year? – Yes,…
2) Had she finished the book before she saw the movie? – Yes,…
3) Had they seen the movie before they read the book? – No,…
4) Had he eaten breakfast before he left for work? – Yes,…
5) Had we met before the party last week? – No,…
4.2 Solution
Exercise 1: Filling in the blanks with the correct verb form
1) By the time arrived at the party, everyone had left.
2) She had studied / had been studying for two hours before she took a break.
3) They had already eaten by the time we got to the restaurant.
4) The movie had started before we arrived at the cinema.
5) He had never seen a bear before he went to Alaska.
Exercise 2: Sentence transformation
1) I had woken up early this morning.
2) They had started the project last week.
3) She had bought a new car yesterday.
4) He had had a sandwich for lunch.
5) We had gone to bed late last night.
Exercise 3: Answering questions
1) Had you ever been to New York before your trip last year?
Yes, I had been to New York before my trip last year.
2) Had she finished the book before she saw the movie?
Yes, she had finished the book before she saw the movie.
3) Had they seen the movie before they read the book?
No, they had not seen the movie before they read the book.
4) Had he eaten breakfast before he left for work?
Yes, he had eaten breakfast before he left for work.
5) Had we met before the party last week?
No, we had not met before the party last week.
5 A story using Past Perfect Tense
And what does the past perfect tense look like in the context of a story? Read and listen to the story. Do you dare to try the comprehension questions too?
Alice had always dreamed of becoming a successful author, but it wasn’t until she had graduated from college that she started to pursue her passion for writing. After completing a few short stories, she had decided to write her first novel. For months, Alice had been working tirelessly, pouring her heart and soul into her writing. She had spent countless hours researching and developing her characters, creating the perfect plot, and editing and revising her work.By the time Alice had submitted her manuscript to various publishing houses, she had been writing for over a year. During this time, she had faced many rejections and setbacks, but she had never given up. She had continued to work hard, honing her craft, and perfecting her novel.
Finally, after what had felt like an eternity, Alice had received an email from a publishing house expressing their interest in publishing her book. She had been overjoyed, and the hours, days, and months she had spent writing had all been worth it. Alice had been ecstatic to see her dream come to fruition.
From that day on, Alice had been known as a successful author, and her book had become a bestseller. Looking back, she had realized that all the hard work, dedication, and perseverance had been worth it.
5.1 Follow-up questions
- 1) What had Alice been dreaming of becoming?
- 2) When had Alice started pursuing her passion for writing?
- 3) Had Alice completed any short stories before deciding to write her first novel?
- 4) How long had Alice been working tirelessly on her writing?
- 5) What had Alice spent countless hours doing while writing her first novel?
- 6) How long had Alice been writing by the time she submitted her manuscript to publishing houses?
- 7) Had Alice faced any rejections or setbacks during her writing process?
- 8) What had Alice continued to do despite the rejections and setbacks she faced?
- 9) How long had Alice been writing before receiving an email from a publishing house expressing their interest in publishing her book?
- 10) What had Alice realized when looking back on all the hard work and perseverance she had put into her writing?
5.2 Answers
- 1) What had Alice been dreaming of becoming?
Alice had been dreaming of becoming a successful author.
- 2) When had Alice started pursuing her passion for writing?
Alice had started pursuing her passion for writing after graduating from college.
- 3) Had Alice completed any short stories before deciding to write her first novel?
Yes, Alice had completed a few short stories before deciding to write her first novel.
- 4) How long had Alice been working tirelessly on her writing?
Alice had been working tirelessly on her writing for months.
- 5) What had Alice spent countless hours doing while writing her first novel?
Alice had spent countless hours researching and developing her characters, creating the perfect plot, and editing and revising her work.
- 6) How long had Alice been writing by the time she submitted her manuscript to publishing houses?
By the time Alice submitted her manuscript to publishing houses, she had been writing for over a year.
- 7) Had Alice faced any rejections or setbacks during her writing process?
Yes, Alice had faced many rejections and setbacks during her writing process.
- 8) What had Alice continued to do despite the rejections and setbacks she faced?
Alice had continued to work hard, honing her craft and perfecting her novel.
- 9) How long had Alice been writing before receiving an email from a publishing house expressing their interest in publishing her book?
Alice had been writing for over a year before receiving an email from a publishing house expressing their interest in publishing her book.
- 10) What had Alice realized when looking back on all the hard work and perseverance she had put into her writing?
Alice had realized that all the hard work, dedication, and perseverance had been worth it when looking back on her journey to becoming a successful author.





